Sometimes it’s useful to be able to map data. That’s why we have Geographic Information Systems, a powerful relational database and information mapping program that takes some training to use and understand.
Luckily for us, ArcGIS offers access maps and mapped data online, on an interface as easy-to-use as Google.
ArcGIS Explorer allows you to not only view different map types, by choosing the basemap, but also to add data on top of the basemap to show information like population density, racial diversity, and median income.
Basic
IMPORTANT: Before you start, it’s good to know that you cannot save a map unless you have a (free) account with ArcGIS online. (Click the “Sign In” button the upper right corner to sign up.)
- From the main page, which shows already-made maps, you can click the “New Map” on the upper left corner to start your own map.
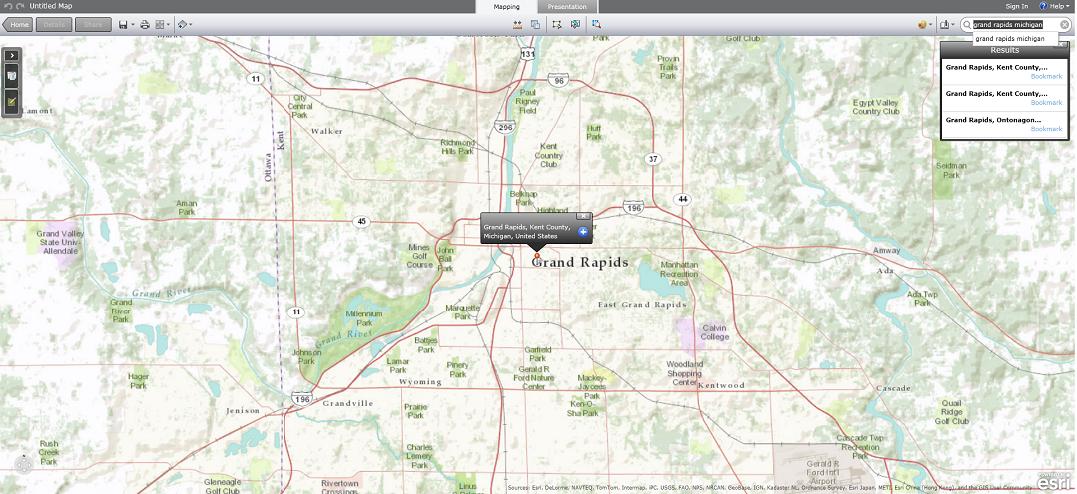
- In the search bar on the upper right corner, put in your town, eg: “Grand Rapids Michigan”
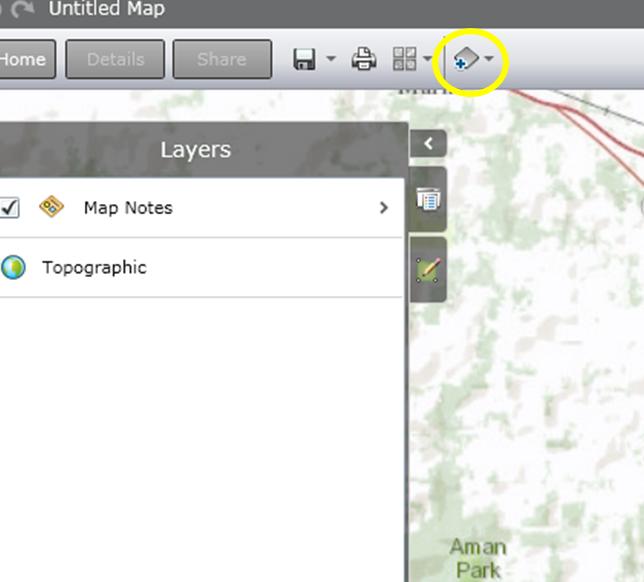
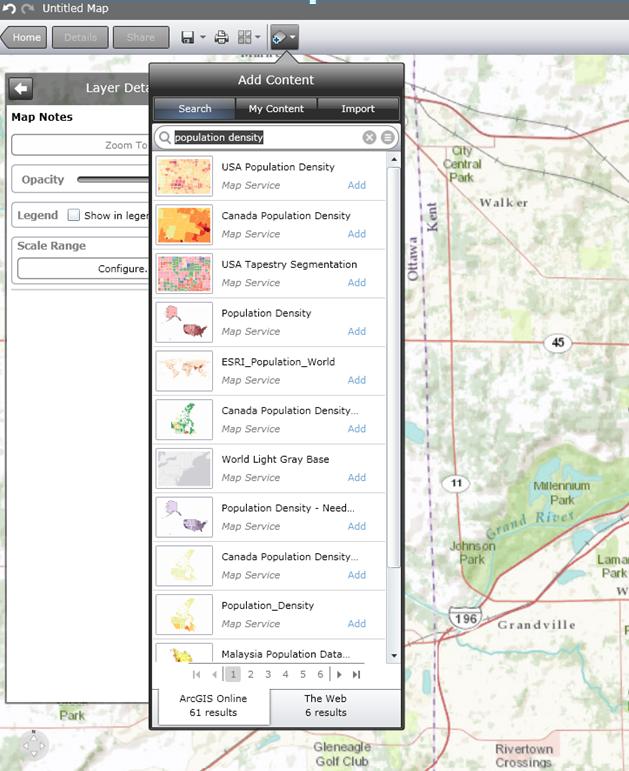
- To add data, click the button on the top that says “Add Content” and search for the type of information you need.
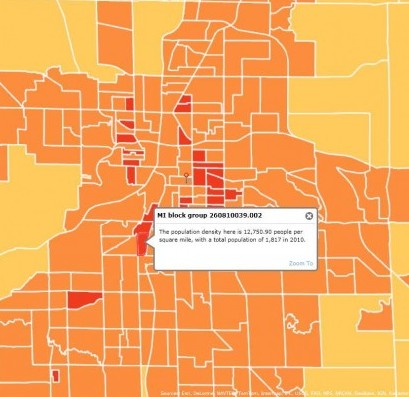
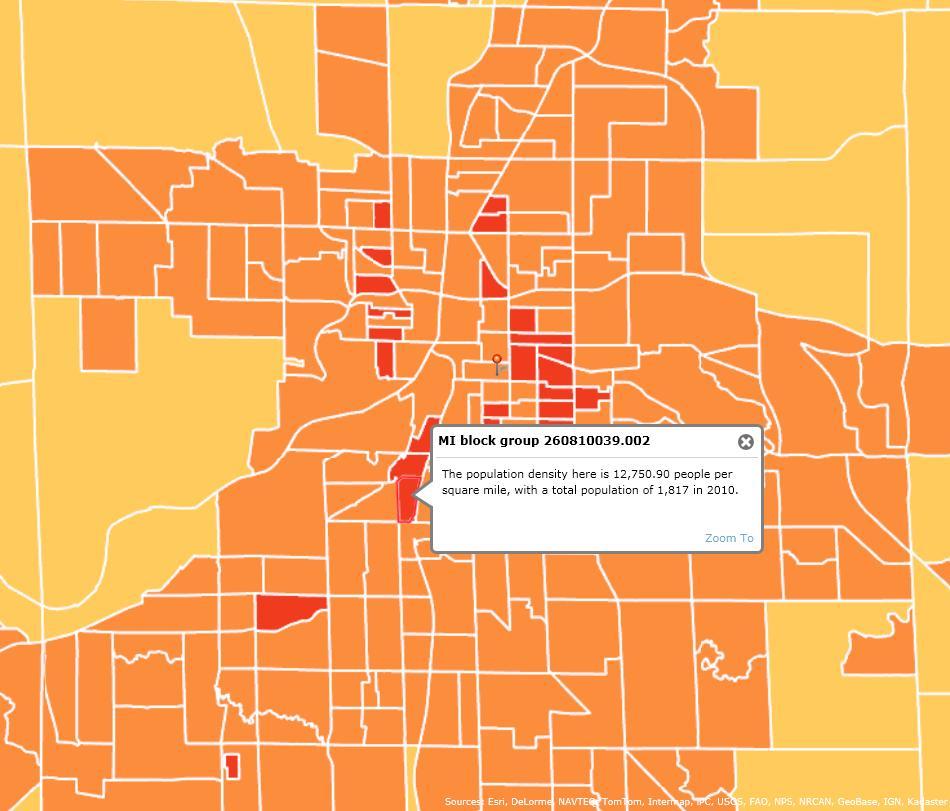
- When you add the layer, it will show up on the map and be listed on the left side of the screen under “Layers.” This is a map of population density. The population density map is overlaying the basemap. You can click on a block group to get specific information.
You can also make the layer less opaque in order to see on or more layers of the map at a time. Click the side arrow of the layer in the Layers sidebar.
- If you press the legend button on the right side of the left sidebar, you can see what the color symbology means.
- You can even add your own “features,” so if you need to map the locations of something specific or a designated area, you can add points and lines to demonstrate them.
Queries
If you want to really get fancy, you can use Queries to highlight only certain data from the layers. Let’s say you want a list of census tracts with a density lower than 100 persons per square mile. Use a query on the Density layer and click on “Tracts.”
The query will ask you to set the parameters. You want to know the population density, so that’s the first thing you choose. You want to know where tracts are fewer than 100 persons per square male, so you choose “is less than” in the second prompt and type “100” into the third. A window will pop up on the right side of the screen, listing all the census tracts.
Measuring Distance and Calculating Area
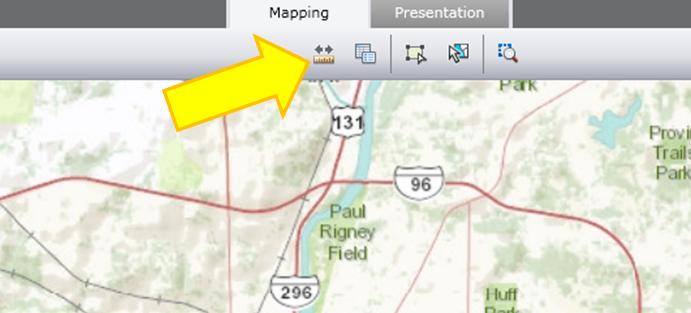
The measure tool is at the top – a ruler with two arrows.
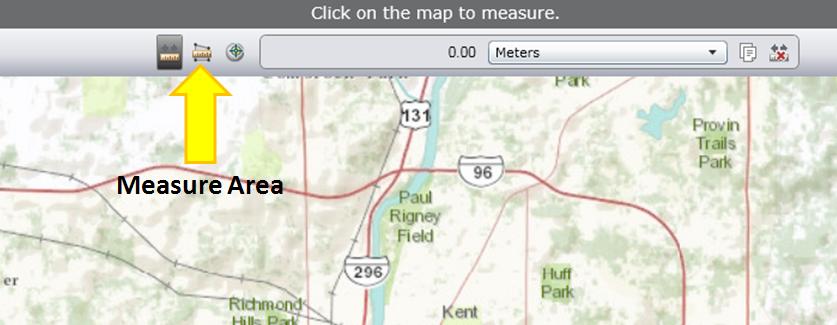
If you click it, you will also have the option to calculate the area using the button next to it, and change the units.
Click one corner of the area you want to measure, then click the next corner, until you have the shape you want. Then click once more on the same spot, and the area calculation should show up at the top with the option to change units.